Difference between revisions of "Mikrotik"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
/ip pool add name=300-BLACK ranges=192.168.1.1-192.168.1.254 | /ip pool add name=300-BLACK ranges=192.168.1.1-192.168.1.254 | ||
| − | DNS Configuration: | + | ==DNS Configuration:== |
| − | /ip dns set allow-remote-requests=yes cache-max-ttl=1w cache-size=5000KiB max-udp- servers=4.4.4.4,8,8.8.8.8packet-size=512 | + | /ip dns set allow-remote-requests=yes cache-max-ttl=1w cache-size=5000KiB max-udp- servers=4.4.4.4,8,8.8.8.8packet-size=512 |
==DHCP Server Configuration for VLAN:== | ==DHCP Server Configuration for VLAN:== | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
*Taken from [[https://cy-wireless.com/blog/mikrotik-router-dhcp-server-configuration-with-vlan https://cy-wireless.com/blog/mikrotik-router-dhcp-server-configuration-with-vlan]] on 10/23/21 | *Taken from [[https://cy-wireless.com/blog/mikrotik-router-dhcp-server-configuration-with-vlan https://cy-wireless.com/blog/mikrotik-router-dhcp-server-configuration-with-vlan]] on 10/23/21 | ||
| + | |||
| + | =VLAN filtering configuration examples= | ||
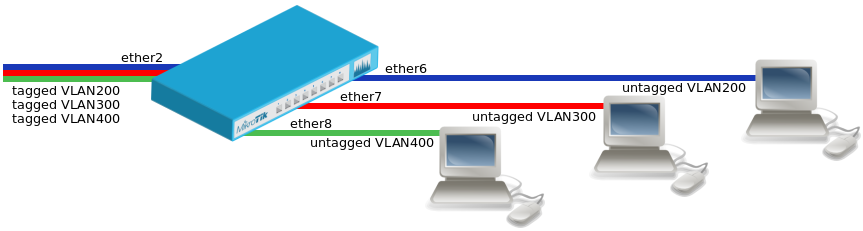
| + | ==VLAN Example #1 (Trunk and Access Ports)== | ||
| + | *Improperly configured bridge VLAN filtering can cause security issues, make sure you fully understand how [https://wiki.mikrotik.com/wiki/Manual:Bridge_VLAN_Table Bridge VLAN table] works before deploying your device into production environments. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Portbased-vlan1.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|Trunk and Access Ports]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Create a bridge with disabled <code>vlan-filtering</code> to avoid losing access to the device before VLANs are completely configured. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface bridge | ||
| + | add name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=no | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Add bridge ports and specify <code>pvid</code> for VLAN access ports to assign their untagged traffic to the intended VLAN. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface bridge port | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether6 pvid=200 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether7 pvid=300 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether8 pvid=400 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Add Bridge VLAN entries and specify tagged and untagged ports in them. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface bridge vlan | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether6 vlan-ids=200 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether7 vlan-ids=300 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether8 vlan-ids=400 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * In the end, when VLAN configuration is complete, enable Bridge VLAN Filtering. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface bridge set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
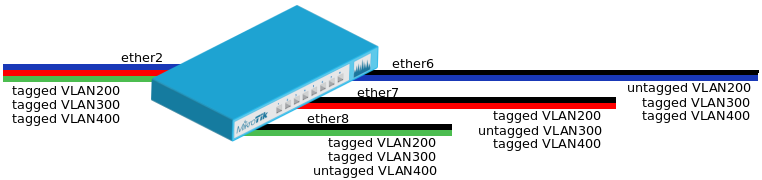
| + | ==VLAN Example #2 (Trunk and Hybrid Ports)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Portbased-vlan2.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|Trunk and Hybrid Ports]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Create a bridge with disabled <code>vlan-filtering</code> to avoid losing access to the router before VLANs are completely configured. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface bridge | ||
| + | add name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=no | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Add bridge ports and specify <code>pvid</code> on hybrid VLAN ports to assign untagged traffic to the intended VLAN. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface bridge port | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether6 pvid=200 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether7 pvid=300 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether8 pvid=400 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Add Bridge VLAN entries and specify tagged and untagged ports in them. In this example egress VLAN tagging is done on ether6,ether7,ether8 ports too, making them into hybrid ports. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface bridge vlan | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2,ether7,ether8 untagged=ether6 vlan-ids=200 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2,ether6,ether8 untagged=ether7 vlan-ids=300 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2,ether6,ether7 untagged=ether8 vlan-ids=400 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * In the end, when VLAN configuration is complete, enable Bridge VLAN Filtering. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface bridge set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *You don't have to add access ports as untagged ports, they will be added dynamically as untagged port with the VLAN ID that is specified in <code>PVID</code>, you can specify just the trunk port as tagged port. All ports that have the same <code>PVID</code> set will be added as untagged ports in a single entry. You must take into account that the bridge itself is a port and it also has a <code>PVID</code> value, this means that the bridge port also will be added as untagged port for the ports that have the same <code>PVID</code>. You can circumvent this behaviour by either setting different <code>PVID</code> on all ports (even the trunk port and bridge itself), or to use <code>frame-type</code> set to <code>accept-only-vlan-tagged</code>. | ||
| + | |||
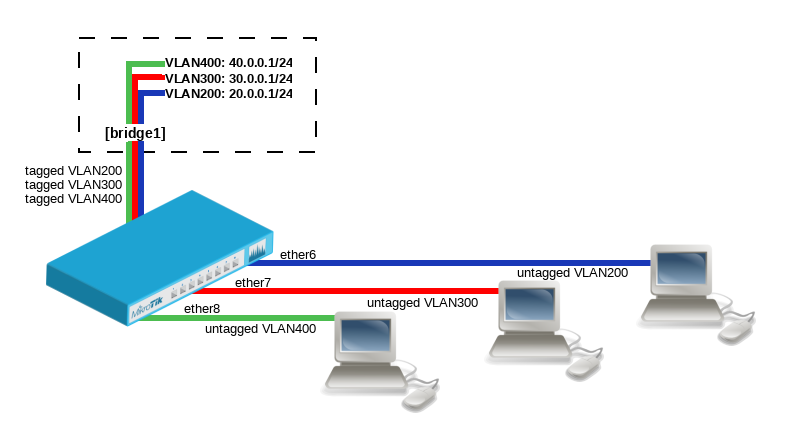
| + | ==VLAN Example #3 (InterVLAN Routing by Bridge)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Bridge-vlan-routing.png|center|frame|alt=Alt text|InterVLAN Routing by Bridge]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Create a bridge with disabled <code>vlan-filtering</code> to avoid losing access to the router before VLANs are completely configured: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface bridge | ||
| + | add name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=no | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add bridge ports and specify <code>pvid</code> for VLAN access ports to assign their untagged traffic to the intended VLAN: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface bridge port | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether6 pvid=200 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether7 pvid=300 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether8 pvid=400 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add Bridge VLAN entries and specify tagged and untagged ports in them. In this example '''bridge1''' interface is the VLAN trunk that will send traffic further to do InterVLAN routing: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface bridge vlan | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 tagged=bridge1 untagged=ether6 vlan-ids=200 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 tagged=bridge1 untagged=ether7 vlan-ids=300 | ||
| + | add bridge=bridge1 tagged=bridge1 untagged=ether8 vlan-ids=400 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Configure VLAN interfaces on the '''bridge1''' to allow handling of tagged VLAN traffic at routing level and set IP addresses to ensure routing between VLANs as planned: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface vlan | ||
| + | add interface=bridge1 name=VLAN200 vlan-id=200 | ||
| + | add interface=bridge1 name=VLAN300 vlan-id=300 | ||
| + | add interface=bridge1 name=VLAN400 vlan-id=400 | ||
| + | |||
| + | /ip address | ||
| + | add address=20.0.0.1/24 interface=VLAN200 | ||
| + | add address=30.0.0.1/24 interface=VLAN300 | ||
| + | add address=40.0.0.1/24 interface=VLAN400 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the end, when VLAN configuration is complete, enable Bridge VLAN Filtering: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | /interface bridge set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
Latest revision as of 22:08, 17 April 2022
Mikrotik Router DHCP Server Configuration with VLAN
IP address Configuration:
/ip address add address=103.7.248.206/29 network=103.7.248.200 broadcast=103.7.248.207 interface=WAN
VLAN Configuration on Mikrotik Router:
/interface vlan add name=100-RED interface=LOCAL vlan-id=100 add name=200-GREEN interface=LOCAL vlan-id=200 add name=300-BLACK interface=LOCAL vlan-id=300 /ip address add address=10.10.10.1/24 interface=100-RED add address=172.16.1.1/24 interface=200-GREEN add address=192.168.1.1/24 interface=300-BLACK
Create an IP address pool:
/ip pool add name=100-RED ranges=10.10.10.1-10.10.10.254 /ip pool add name=200-GREEN ranges=172.16.1.1-172.16.1.254 /ip pool add name=300-BLACK ranges=192.168.1.1-192.168.1.254
DNS Configuration:
/ip dns set allow-remote-requests=yes cache-max-ttl=1w cache-size=5000KiB max-udp- servers=4.4.4.4,8,8.8.8.8packet-size=512
DHCP Server Configuration for VLAN:
/ip dhcp-server enable 0 /ip dhcp-server add interface = LOCAL address-pool = 100-RED /ip dhcp-server add interface = LOCAL address-pool = 200-GREEN /ip dhcp-server add interface = LOCAL address-pool = 300-BLACK /ip dhcp-server network add address = 10.10.10.0/24 gateway = 10.10.10.1 dns-server = 8.8.8.8 comment=”100-RED” /ip dhcp-server network add address = 172.16.1.0/24 gateway = 172.16.1.1 dns-server = 8.8.8.8 comment=”200-GREEN” /ip dhcp-server network add address = 192.168.1.0/24 gateway = 192.168.1.1 dns-server = 8.8.8.8 comment=”300-BLACK”
NAT Configuration:
/ip firewall nat add chain=srcnat action=masquerade src-address=192.168.1.0/24 out-interface=WAN add chain=srcnat action=masquerade src-address=172.16.1.0/24 out-interface=WAN add chain=srcnat action=masquerade src-address=10.10.10.0/24 out-interface=WAN
Default Gateway Setup:
/ip route add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=103.7.248.201
- Taken from [https://cy-wireless.com/blog/mikrotik-router-dhcp-server-configuration-with-vlan] on 10/23/21
VLAN filtering configuration examples
VLAN Example #1 (Trunk and Access Ports)
- Improperly configured bridge VLAN filtering can cause security issues, make sure you fully understand how Bridge VLAN table works before deploying your device into production environments.
- Create a bridge with disabled
vlan-filteringto avoid losing access to the device before VLANs are completely configured.
/interface bridge add name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=no
- Add bridge ports and specify
pvidfor VLAN access ports to assign their untagged traffic to the intended VLAN.
/interface bridge port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether6 pvid=200 add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether7 pvid=300 add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether8 pvid=400
- Add Bridge VLAN entries and specify tagged and untagged ports in them.
/interface bridge vlan add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether6 vlan-ids=200 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether7 vlan-ids=300 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2 untagged=ether8 vlan-ids=400
- In the end, when VLAN configuration is complete, enable Bridge VLAN Filtering.
/interface bridge set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes
VLAN Example #2 (Trunk and Hybrid Ports)
- Create a bridge with disabled
vlan-filteringto avoid losing access to the router before VLANs are completely configured.
/interface bridge add name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=no
- Add bridge ports and specify
pvidon hybrid VLAN ports to assign untagged traffic to the intended VLAN.
/interface bridge port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether2 add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether6 pvid=200 add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether7 pvid=300 add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether8 pvid=400
- Add Bridge VLAN entries and specify tagged and untagged ports in them. In this example egress VLAN tagging is done on ether6,ether7,ether8 ports too, making them into hybrid ports.
/interface bridge vlan add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2,ether7,ether8 untagged=ether6 vlan-ids=200 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2,ether6,ether8 untagged=ether7 vlan-ids=300 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=ether2,ether6,ether7 untagged=ether8 vlan-ids=400
- In the end, when VLAN configuration is complete, enable Bridge VLAN Filtering.
/interface bridge set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes
- You don't have to add access ports as untagged ports, they will be added dynamically as untagged port with the VLAN ID that is specified in
PVID, you can specify just the trunk port as tagged port. All ports that have the samePVIDset will be added as untagged ports in a single entry. You must take into account that the bridge itself is a port and it also has aPVIDvalue, this means that the bridge port also will be added as untagged port for the ports that have the samePVID. You can circumvent this behaviour by either setting differentPVIDon all ports (even the trunk port and bridge itself), or to useframe-typeset toaccept-only-vlan-tagged.
VLAN Example #3 (InterVLAN Routing by Bridge)
Create a bridge with disabled vlan-filtering to avoid losing access to the router before VLANs are completely configured:
/interface bridge add name=bridge1 vlan-filtering=no
Add bridge ports and specify pvid for VLAN access ports to assign their untagged traffic to the intended VLAN:
/interface bridge port add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether6 pvid=200 add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether7 pvid=300 add bridge=bridge1 interface=ether8 pvid=400
Add Bridge VLAN entries and specify tagged and untagged ports in them. In this example bridge1 interface is the VLAN trunk that will send traffic further to do InterVLAN routing:
/interface bridge vlan add bridge=bridge1 tagged=bridge1 untagged=ether6 vlan-ids=200 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=bridge1 untagged=ether7 vlan-ids=300 add bridge=bridge1 tagged=bridge1 untagged=ether8 vlan-ids=400
Configure VLAN interfaces on the bridge1 to allow handling of tagged VLAN traffic at routing level and set IP addresses to ensure routing between VLANs as planned:
/interface vlan add interface=bridge1 name=VLAN200 vlan-id=200 add interface=bridge1 name=VLAN300 vlan-id=300 add interface=bridge1 name=VLAN400 vlan-id=400 /ip address add address=20.0.0.1/24 interface=VLAN200 add address=30.0.0.1/24 interface=VLAN300 add address=40.0.0.1/24 interface=VLAN400
In the end, when VLAN configuration is complete, enable Bridge VLAN Filtering:
/interface bridge set bridge1 vlan-filtering=yes